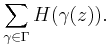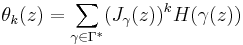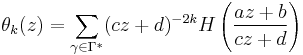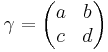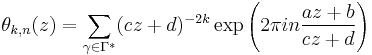Poincaré series (modular form)
In number theory, a Poincaré series is a mathematical series generalizing the classical theta series that is associated to any discrete group of symmetries of a complex domain, possibly of several complex variables. In particular, they generalize classical Eisenstein series. They are named after Henri Poincaré.
If Γ is a finite group acting on a domain D and H(z) is any meromorphic function on D, then one obtains an automorphic function by averaging over Γ:
However, if Γ is a discrete group, then additional factors must be introduced in order to assure convergence of such a series. To this end, a Poincaré series is a series of the form
where Jγ is the Jacobian determinant of the group element γ,[1] and the asterisk denotes that the summation takes place only over coset representatives yielding distinct terms in the series.
The classical Poincaré series of weight 2k of a Fuchsian group Γ is defined by the series
the summation extending over congruence classes of fractional linear transformations
belonging to Γ. Choosing H to be a character of the cyclic group of order n, one obtains the so-called Poincaré series of order n:
The latter Poincaré series converges absolutely and uniformly on compacta (in the upper halfplane), and is a modular form of weight 2k for Γ. Note that, when Γ is the full modular group and n = 0, one obtains the Eisenstein series of weight 2k. In general, the Poincaré series is, for n ≥ 1, a cusp form.
Notes
- ^ Or a more general factor of automorphy as discussed in Kollár 1995, §5.2.
References
- Kollár, János (1995), Shafarevich maps and automorphic forms, M. B. Porter Lectures, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-04381-4, MR1341589.
- Solomentsev, E.D. (2001), "Theta-series", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=T/t092610.